Abstract
In this study, we evaluated the caprylic acid-based oil-in-water (O/W) emulsion-assisted extraction of lycopene from tomatoes. Emulsion-assisted extraction was performed using two types of micron-sized O/W emulsions: (a) O/W emulsion with absence or (b) presence of 0.1% (w/w) of Tween 20 emulsifier. This green extraction technique was compared with the conventional method using soybean oil, tributyrin, and caprylic acid. The results show that caprylic acid, a green solvent, is significantly more effective for lycopene recovery than soybean oil and tributyrin. In the absence of an emulsifier, caprylic acid-based O/W emulsion significantly improved the lycopene content by 14.69 mg/g, corresponding to a 98.59% extraction efficiency at 50 ˚C. The capability of the proposed approach to lycopene recovery was explained in terms of lycopene affinity, the ability to swell the tomato cell, and some other standard parameters. In addition, caprylic acid has the significant advantage that once developed with the extracted lycopene can be used directly as a food additive.




Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- O/W emulsion:
-
Oil-in-water emulsion
- w/w:
-
Weight-per-weight basis
- \({C}_{UV}\) :
-
Lycopene content in the extract (mg/mL)
- \(V\) :
-
Volume of total extract (mL)
- \(m\) :
-
Dry weight of tomato powder (g)
- \(Y\) :
-
Yield of lycopene extraction (%)
- \({d}_{\mathrm{4,3}}\) :
-
Volume mean diameter
- D :
-
Distance in Hansen space (MPa0.5)
- δ:
-
Solubility of a molecule
- \(\Delta E\) :
-
Cohesive energy
- \({v}_{m}\) :
-
Molar volume
- \({\delta }_{D}\) :
-
Dispersion-bonding solubility
- \({\delta }_{P},\) :
-
Polar -bonding solubility
- \({\delta }_{H}\) :
-
Hydrogen-bonding solubility
References
Abbasi S, Radi M (2016) Food grade microemulsion systems: canola oil/lecithin:n-propanol/water. Food Chem 194:972–979. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.08.078
Amiri-Rigi A, Abbasi S (2016) Microemulsion-based lycopene extraction: effect of surfactants, co-surfactants and pretreatments. Food Chem 197:1002–1007. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.11.077
Amiri-Rigi A, Abbasi S (2019) Extraction of lycopene using a lecithin-based olive oil microemulsion. Food Chem 272:568–573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.08.080
Baysal T, Ersus S, Starmans DAJ (2000) Supercritical CO2 extraction of β-carotene and lycopene from tomato paste waste. J Agric Food Chem 48(11):5507–5511. https://doi.org/10.1021/JF000311T
Delgado Naranjo JM, Jiménez Callejón MJ, Peñuela Vásquez M, Rios LA, Robles Medina A (2021) Optimization of the enzymatic synthesis of structured triacylglycerols rich in docosahexaenoic acid at sn-2 position by acidolysis of aurantiochytrium limacinum SR21 oil and caprylic acid using response surface methodology. J Appl Phycol 33(4):2031–2045. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-021-02464-6
Dehghan-Shoar Z, Hardacre AK, Meerdink G, Brennan CS (2011) Lycopene extraction from extruded products containing tomato skin. Int J Food Sci Techno 46(2):365–371. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2621.2010.02491.x
de la Peña-Gil A, Toro-Vazquez JF, Rogers MA (2016) Simplifying hansen solubility parameters for complex edible fats and oils. Food Biophys 11(3):283–291. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-016-9440-9
Deng Y, Zhao S, Yang X, Hou F, Fan L, Wang W, Xu E, Cheng H, Guo M, Liu D (2021) Evaluation of extraction technologies of lycopene: hindrance of extraction, effects on isomerization and comparative analysis - a review. Trends Food Sci Technol 115:285–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2021.06.051
Diacon A, Călinescu I, Vinatoru M, Chipurici P, Vlaicu A, Cristian Boscornea A, Mason TJ (2021) Fatty acid ethyl esters (FAEE): a new, green and renewable solvent for the extraction of carotenoids from tomato waste products. Molecules 26(14):4388. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26144388
Eh ALS, Teoh SG (2012) Novel modified ultrasonication technique for the extraction of lycopene from tomatoes. Ultrason Sonochem 19(1):151–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2011.05.019
Eiteman MA, Goodrum JW (1994) Density and viscosity of low-molecular weight triglycerides and their mixtures. J Am Oil Chem Soc 71(11):1261–1265. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02540548
Fidale LC, Ruiz N, Heinze T, El Seoud OA (2008) Cellulose swelling by aprotic and protic solvents: what are the similarities and differences? Macromol Chem Phys 209(12):1240–1254. https://doi.org/10.1002/macp.200800021
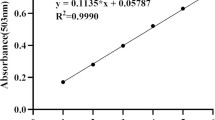
Fish WW, Perkins-Veazie P, Collins JK (2002) A quantitative assay for lycopene that utilizes reduced volumes of organic solvents. J Food Compost Anal 15(3):309–317. https://doi.org/10.1006/jfca.2002.1069
Flanagan J, Kortegaard K, Neil Pinder D, Rades T, Singh H (2006) Solubilisation of soybean oil in microemulsions using various surfactants. Food Hydrocoll 20(2–3 SPEC. ISS.):253–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2005.02.017
Goula AM, Ververi M, Adamopoulou A, Kaderides K (2017) Green ultrasound-assisted extraction of carotenoids from pomegranate wastes using vegetable oils. Ultrason Sonochem 34:821–830. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ULTSONCH.2016.07.022
Grunin LY, Grunin YB, Talantsev VI, Nikolskaya EA, Masas DS (2015) Features of the structural organization and sorption properties of cellulose. Polym Sci Ser A+ 57(1):43–51. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0965545X15010034
Hansen CM (2007) Hansen solubility parameters : a user’s handbook, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, USA
Hildebrand JH, Scott RL (1964) The solubility of nonelectrolytes, 3rd edn. Dover Publications, New York, NY
Lavecchia R, Zuorro A (2016) Cellulase applications in pigment and bioactive compound extraction. In: Gupta VK (ed) New and future developments in microbial biotechnology and bioengineering: microbial cellulase system properties an applications. Elsevier, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, pp 209–222
Lee HS, Roy A, Lane O, Dunn S, McGrath JE (2008) Hydrophilic–hydrophobic multiblock copolymers based on poly(arylene ether sulfone) via low-temperature coupling reactions for proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Polymer 49(3):715–723. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.POLYMER.2007.12.023
Li N, Wu X, Zhuang W, Xia L, Chen Y, Wu C, Rao Z, Du L, Zhao R, Yi M, Wan Q, Zhou Y (2021) Tomato and lycopene and multiple health outcomes: umbrella review. Food Chem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128396
Mantanis GI, Young RA, Rowell RM (1994) Swelling of wood - Part 1. swelling in water. Wood Sci Technol 28(2):119–134. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00192691
Nordoy A, Barstad L, Connor WE, Hatcher L (1991) Absorption of the n−3 eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids as ethyl esters and triglycerides by humans. Am J Clin Nutr 53(5):1185–1190. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/53.5.1185
Ortiz-Tafoya MC, Tecante A (2018) Physicochemical characterization of sodium stearoyl lactylate (SSL), polyoxyethylene sorbitan monolaurate (Tween 20) and κ-carrageenan. Data Brief 19:642–650. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dib.2018.05.064
Pierre FX, Souchon I, Athes-Dutour V, Marin M (2002) Membrane-based solvent extraction of sulfur aroma compounds: influence of operating conditions on mass transfer coefficients in a hollow fiber contactor. Desalination 148(1–3):199–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0011-9164(02)00698-7
Prusov AN, Prusova SM, Zakharov AG (2014) Interaction of cellulose and lignocellulosic polymers with water and aqueous systems. Russ Chem Bull 63(9):1926–1945. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11172-014-0683-7
Roohinejad S, Oey I, Everett DW, Niven BE (2014) Evaluating the effectiveness of β-carotene extraction from pulsed electric field-treated carrot pomace using oil-in-water microemulsion. Food Bioproc Tech 7(11):3336–3348. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-014-1334-6
Shakeel F, Alshehri S, Ibrahim MA, Altamimi M, Haq N, Elzayat EM, Shazly GA (2021) Solubilization and thermodynamic properties of simvastatin in various micellar solutions of different non-ionic surfactants: computational modeling and solubilization capacity. PLoS ONE 16:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0249485
Taoukis D, Assimakopoulos J (2010) Effect of growth season and slow-release fertilizers on quality characteristics of tomatoes. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 41(8):945–955. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103621003646030
Torres-Valenzuela LS, Ballesteros-Gómez A, Rubio S (2020) Supramolecular solvent extraction of bioactives from coffee cherry pulp. J Food Eng 278:109933. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JFOODENG.2020.109933
Tsogtoo B, Taarji N, Melanie H, Khalid N, Tsolmon S, Kobayashi I, Neves MA, Nakajima M (2020) Emulsion-based extraction of β-sitosterol and carotenoids from sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides) pomace. Int Food Res J 27(1):56–65
Vági E, Simándi B, Vásárhelyiné KP, Daood H, Kéry Á, Doleschall F, Nagy B (2007) Supercritical carbon dioxide extraction of carotenoids, tocopherols and sitosterols from industrial tomato by-products. J Supercrit Fluids 40(2):218–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.supflu.2006.05.009
Yamamoto H, Abbott S, Hansen CM (2017) Consideration of hansen solubility parameters. part 1 dividing the dispersion term (δD) and new HSP distance. Hansen Solubility Parameters 50th Anniversary Conference 13:1–13
Zhang J, Li L, Boonkerd K, Kim JK (2014) Formation of SBS triblock copolymers using waste soybean oil as coupling agent. J Appl Polym Sci 131(17):8544–8554. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.40684
Zuorro A (2020) Enhanced lycopene extraction from tomato peels by optimized mixed-polarity solvent mixtures. Molecules 25(9):2038. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25092038
Acknowledgements
All co-authors are dully acknowledged for their valuable contribution, as follows: KK conceived the idea, carried out the experiments, and wrote the manuscript. SE and NT analyzed the data and edited the manuscript. MSRS analyzed the data. IK designed the experiment. MN designed the experiment and interpreted the results. MAN supervised the work and edited the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KK experimental design, carried out the experiments, and wrote the manuscript. SE and NT analyzed the data and edited the manuscript. MSRS analyzed the data. IK designed the experiment. MN conceiving the idea, and interpretation of the results. MAN experimental design, supervised the work and edited the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khadizatul, K., Elshamy, S., Taarji, N. et al. Revisiting lycopene extraction: Caprylic acid-based emulsion for the highest recovery. J Food Sci Technol 59, 4427–4435 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-022-05522-0
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-022-05522-0