Abstract
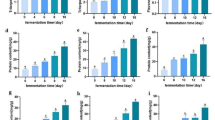
Edible fungi by-products are fruiting body residues produced during the production of hot pot base. There are abundant cellulose, protein, and minerals remained in edible fungi by-products. Ultrasonic-assisted two-stage enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulase, pectinase, and papain was optimized for the purpose of extracting its soluble substances. The taste, flavor, antioxidant capacity, color, soluble solids, soluble protein, conductivity, and turbidity of the optimized edible fungi by-product hydrolysate (EFBH) were evaluated. It was found that the soluble solids content and antioxidant activity of the optimized EFBH were significantly increased, and the flavor change was insignificant. The optimized EFBH with low bitterness and high umami taste was obtained through the two-stage enzymatic hydrolysis, and its soluble solids content was increased by 2.87 times, and the umami response value was increased by 12.19 times.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data are available from the corresponding author upon suitable request.
References
Abou-Diab, M., Thibodeau, J., Fliss, I., Dhulster, P., Nedjar, N., & Bazinet, L. (2021). Impact of conductivity on the performances of electro-acidification and enzymatic hydrolysis phases of bovine hemoglobin by electrodialysis with bipolar membranes for the production of bioactive peptides. Separation and Purification Technology, 269.
Akaberi, S., Gusbeth, C., Silve, A., Senthilnathan, D. S., Navarro-López, E., Molina-Grima, E., Müller, G., & Frey, W. (2019). Effect of pulsed electric field treatment on enzymatic hydrolysis of proteins of Scenedesmus almeriensis. Algal Research, 43.
Alzorqi, I., Sudheer, S., Lu, T. J., & Manickam, S. (2017). Ultrasonically extracted beta-d-glucan from artificially cultivated mushroom, characteristic properties and antioxidant activity. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 35(Pt B), 531–540.
Ang, S. S., & Ismail-Fitry, M. R. (2019). Production of different mushroom protein hydrolysates as potential flavourings in chicken soup using stem bromelain hydrolysis. Food Technology and Biotechnology, 57(4), 472–480.
Arilla, E., Igual, M., Martinez-Monzo, J., Codoner-Franch, P., & Garcia-Segovia, P. (2020). Impact of resistant maltodextrin addition on the physico-chemical properties in pasteurised orange juice. Foods, 9(12).
Badr, A., Abdel-Razek, A., Youssef, M., Shehata, M., Hassanein, M., & Amra, H. (2020). Natural antioxidants: Preservation roles and mycotoxicological safety of food. Egyptian Journal of Chemistry, 0(0), 0–0.
Bhotmange, D. U., Wallenius, J. H., Singhal, R. S., & Shamekh, S. S. (2017). Enzymatic extraction and characterization of polysaccharide from Tuber aestivum. Bioactive Carbohydrates and Dietary Fibre, 10, 1–9.
Byun, T., Kofod, L., & Blinkovsky, A. (2001). Synergistic action of an X-prolyl dipeptidyl aminopeptidase and a non-specific aminopeptidase in protein hydrolysis. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 49(4), 2061–2063.
Chen, F., Zhang, M., & Yang, C.-h. (2020). Application of ultrasound technology in processing of ready-to-eat fresh food: A review. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 63.
Chen, K., Zhang, M., Adhikari, B., & Wang, M. (2022). Microencapsulation of Sichuan pepper essential oil in soybean protein isolate—Sichuan pepper seed soluble dietary fiber complex coacervates. Food Hydrocolloids, 125.
Delgado-Aguilar, M., Valverde-Som, L., & Cuadros-Rodríguez, L. (2018). Solver, an Excel application to solve the difficulty in applying different univariate linear regression methods. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 178, 39–46.
Fan, K., Zhang, M., & Jiang, F. (2019). Ultrasound treatment to modified atmospheric packaged fresh-cut cucumber: Influence on microbial inhibition and storage quality. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 54, 162–170.
Fu, Y., Liu, J., Zhang, W., Waehrens, S. S., Tostesen, M., Hansen, E. T., Bredie, W. L. P., & Lametsch, R. (2020). Exopeptidase treatment combined with Maillard reaction modification of protein hydrolysates derived from porcine muscle and plasma: Structure-taste relationship. Food Chemistry, 306, 125613.
Gao, J., Fang, D., Muinde Kimatu, B., Chen, X., Wu, X., Du, J., Yang, Q., Chen, H., Zheng, H., An, X., Zhao, L., & Hu, Q. (2021). Analysis of umami taste substances of morel mushroom (Morchella sextelata) hydrolysates derived from different enzymatic systems. Food Chemistry, 362, 130192.
GB5009.3. (2016). National food safety standards: Determination of moisture in food [S]. Beijing: Chnia Standard Press.
GB5009.4. (2016). National food safety standards: Determination of ash in food [S]. Beijing: Chnia Standard Press.
GB5009.5. (2016). National food safety standards: Determination of protein in food [S]. Beijing: Chnia Standard Press.
GB5009.6. (2016). National food safety standards: Determination of fat in food [S]. Beijing: Chnia Standard Press.
GB/T15672. (2009). National food safety standards: Determination of total sugar in food [S]. Beijing: Chnia Standard Press.
Hao, S., Min, Z., & Benu, A. (2018). Advances of electronic nose and its application in fresh foods: A review. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 58(16), 2700–2710.
Hefferon, K., Cantero-Tubilla, B., Badar, U., & Wilson, D. W. (2020). Plant-based cellulase assay systems as alternatives for synthetic substrates. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 192(4), 1318–1330.
Hongyao, J., Min, Z., Bhesh, B., & Benu, A. (2018). Application of electronic tongue for fresh foods quality evaluation: A review. Food Reviews International, 34(8), 746–769.
Hou, L., Zhang, Y., Li, C., Wang, X., & Wang, S. C. (2021). Determination of main bitter compounds in soaked and germinated sesame pastes. Journal of Oleo Science, 70(1), 31–38.
Huang, X., Kou, X., Wang, L., Ji, R., Ma, C., & Wang, H. (2019). Effective hydroxylation of tangeretin from Citrus Peel (Chenpi) by edible acids and its improvement in antioxidant and anti-lipase activities. Lwt-Food Science and Technology, 116.
Linlin, L., Min, Z., & Peiqiang, Y. (2019). Suitability of LF-NMR to analysis water state and predict dielectric properties of Chinese yam during microwave vacuum drying. LWT -- Food Science and Technology, 105, 257–264.
Łubek-Nguyen, A., Ziemichód, W., & Olech, M. (2022). Application of enzyme-assisted extraction for the recovery of natural bioactive compounds for nutraceutical and pharmaceutical applications. Applied Sciences, 12(7).
Mitic, V., Ilic, M., Dimitrijevic, M., Cvetkovic, J., Ciric, S., & Jovanovic, V. S. (2015). Chemometric characterization of peach, nectarine and plum cultivars according to fruit phenolic content and antioxidant activity. Fruits, 71(1), 57–66.
Murray, A. F., Wickramasinghe, P. C. K., & Munafo, J. P., Jr. (2020). Key odorants from the fragrant bolete Suillus Punctipes. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 68(32), 8621–8628.
Nasiru, M. M., Boateng, E. F., Wang, Z., Yan, W., Zhuang, H., & Zhang, J. (2022). Ultrasound-assisted high-voltage cold atmospheric plasma treatment on the inactivation and structure of lysozyme: Effect of treatment voltage. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 15(8), 1866–1880.
Ning, M., Li-li, Q., Ze-hua, Z., Xiang, G., Hong-shan, P., Hui-hua, Z., Dong-lu, F., Li-yan, Z., & Mei-xia, Z. (2020). Analysis of nutritional quality and characteristic flavor composition of edible mushrooms compound instant coarse cereal flour. Science and Technology of Food Industry, (3), 251–258.
Noguera, N. H., Lima, D. C., Filho, E. G. A., Fonteles, T. V., & Rodrigues, S. (2021). Influence of different non-thermal processing on guava, orange, and tangerine juices and the food matrix effects. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 14(9), 1662–1672.
Polanco-Lugo, E., Davila-Ortiz, G., Abram Betancur-Ancona, D., & Antonio Chel-Guerrero, L. (2014). Effects of sequential enzymatic hydrolysis on structural, bioactive and functional properties of Phaseolus lunatus protein isolate. Food Science and Technology, 34(3), 441–448.
Poojary, M. M., Orlien, V., Passamonti, P., & Olsen, K. (2017). Enzyme-assisted extraction enhancing the umami taste amino acids recovery from several cultivated mushrooms. Food Chemistry, 234, 236–244.
Qing, S., Min, Z., Mujumdar, A. S., & Peiqiang, Y. (2019). Combined LF-NMR and artificial intelligence for continuous real-time monitoring of carrot in microwave vacuum drying. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 12(4), 551–562.
Radi, M., Ahmadi, H., & Amiri, S. (2022). Effect of cinnamon essential oil-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC) against Penicillium citrinum and Penicillium expansum involved in tangerine decay. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 15(2), 306–318.
Singla, R., Ganguli, A., & Ghosh, M. (2012). Physicochemical and nutritional characteristics of organic acid-treated button mushrooms (Agaricus bisporous). Food and Bioprocess Technology, 5(2), 808–815.
Su, Y., Zhang, M., Bhandari, B., & Zhang, W. (2018). Enhancement of water removing and the quality of fried purple-fleshed sweet potato in the vacuum frying by combined power ultrasound and microwave technology. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 44, 368–379.
Sun, L., Xin, G., Hou, Z., Zhao, X., Xu, H., Bao, X., Xia, R., Li, Y., & Li, L. (2021). Biosynthetic mechanism of key volatile biomarkers of harvested Lentinula edodes triggered by spore release. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry, 69(32), 9350–9361.
Sun, Q., Zhang, M., & Mujunndar, A. S. (2019). Recent developments of artificial intelligence in drying of fresh food: A review. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 59(14), 2258–2275.
Tian, B., Pan, Y., Wang, J., Cai, M., Ye, B., Yang, K., & Sun, P. (2022). Insoluble dietary fibers from by-products of edible fungi industry: Basic structure, physicochemical properties, and their effects on energy intake. Frontiers in Nutrition, 9, 851228.
Tsikrika, K., Lemos, M. A., Chu, B.-S., Bremner, D. H., & Hungerford, G. (2022). Effect of ultrasound on the activity of mushroom (Agaricus bisporous) polyphenol oxidase and observation of structural changes using time-resolved fluorescence. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 15(3), 656–668.
Usmani, S., Hussain, A., Wahab, S., Kushwaha, P., Khatoon, S., Arif, M., Prakash, O., & Kamal, M. (2021). Antioxidant potential of crude extract, flavonoid-rich fractions, and a new compound from the seeds of Cordia dichotoma. Indian Journal of Natural Products and Resources, 12(3), 437–444.
Vassilev, S. V., Menendez, R., Diaz-Somoano, M., & Martinez-Tarazona, M. R. (2004). Phase-mineral and chemical composition of coal fly ashes as a basis for their multicomponent utilization. 2. Characterization of ceramic cenosphere and salt concentrates. Fuel, 83(4–5), 585–603.
Wang, K., Wang, C., Liu, Y., Jiang, W., Li, W., Cheng, F., Ma, C., & Nie, Y. (2021). Effects of hydrogen sulfide on the quality deterioration of button mushrooms and the interaction with ethylene. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 14(11), 1983–1995.
Xi-Jia, Z., Min, Z., Bimal, C., Sakamon, D., & Zhimei, G. (2022). Novel combined use of red-white LED illumination and modified atmosphere packaging for maintaining storage quality of postharvest pakchoi. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 15(3), 590–605.
Xiao-Fei, W., Min, Z., & Zhongqin, L. (2019). Influence of infrared drying on the drying kinetics, bioactive compounds and flavor of Cordyceps militaris. LWT -- Food Science and Technology, 111, 790–798.
Yan-yan, R., Ting-ting, Z., Hui-hui, Z., Jun-xian, G., & Wei-hua, L. (2018). Research of enzymatic preparation of Lentinus edodes extraction. China Food Additives, (6), 66–72.
Yanan, S., Min, Z., & Zhongxiang, F. (2020). Efficient physical extraction of active constituents from edible fungi and their potential bioactivities: A review. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 105, 468–482.
Yu, M., He, S., Tang, M., Zhang, Z., Zhu, Y., & Sun, H. (2018). Antioxidant activity and sensory characteristics of Maillard reaction products derived from different peptide fractions of soybean meal hydrolysate. Food Chemistry, 243, 249–257.
Yu, Q., Guo, M., Zhang, B., Wu, H., Zhang, Y., Zhang, L., & El-Demerdash, F. M. (2020). Analysis of nutritional composition in 23 kinds of edible fungi. Journal of Food Quality, 2020, 1–9.
Zhang, L., Zhang, M., & Mujumdar, A. S. (2021). Development of flavor during drying and applications of edible mushrooms: A review. Drying Technology, 39(11), 1685–1703.
Zhu, Y., Zhang, M., Zhang, L., Law, C. L., Wang, Y., & Liu, K. (2022). Preparation of enzymatic hydrolysate using edible fungi by-products of soup seasoning: Effect of different enzymes on enzymatic hydrolysis. Food Bioscience, 49.
Funding
We acknowledge the financial supports from National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2018YFD0700303), Jiangsu Province Key Laboratory Project of Advanced Food Manufacturing Equipment and Technology (No. FMZ202003), Jiangsu Province (China) Key Project in Agriculture (Contract No. BE2015310217), and National First-Class Discipline Program of Food Science and Technology (No. JUFSTR20180205). All these above enable us to carry out and promote this research smoothly.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
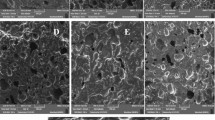
YZ finished the data analysis, figures drawing, and the main manuscript text writing; CLL, MZ, and YW reviewed and revised the manuscript; KL provided the information of raw materials and assisted in providing Fig. 1; the supervision, project administration, and final revision of the manuscript were finished by MZ and YZ. All authors reviewed the manuscript and agreed to publish this version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, Y., Zhang, M., Law, C.L. et al. Optimization of Ultrasonic-Assisted Enzymatic Hydrolysis to Extract Soluble Substances from Edible Fungi By-products. Food Bioprocess Technol 16, 167–184 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-022-02930-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-022-02930-0