Abstract
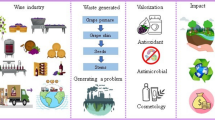
Grape is one of the most well-known fruits worldwide, being transformed into distinct food products, one of which is wine. A significantly large portion of grape production is exclusively destined for winemaking which, as an industrial process, produces significant amounts of by-products. Grape pomace is considered the major by-product of winemaking and consists of skins, seeds and stems that are left behind after the stage of grapes’ pressing. According to the Waste Framework Directive (Directive 2008/98/EC) of the European Parliament, “waste prevention should be the first priority of waste management and re-use and material recycling should be preferred to energy recovery from waste”. This review aims to approach the recent advances over the valorization of grape pomace as a value-adding material, exploring its potential uses in the industry. The main methods for this purpose are discussed, including traditional methods (such as distillates production, animal feed, and soil fertilizer), its use as a technological aid in different industrial processes (e.g., adsorption, immobilization, food packaging and cosmetics), its addition in food products, highlighting its potential effects on physicochemical, functional and sensory attributes of these products, and as a raw material for bioenergy production. The large number of strategies that have been employed for the possible use of grape pomace show its high revalorization potential, with studies being conducted on several different food products of different categories, such as dairy, meat, fish and bakery products or even wine itself. The main positive effect of this addition consists the increase of the antioxidant activity of the medium, contributing towards enhanced shelf-life, both microbiologically and physicochemically. Given the fact that a linear production model is not satisfactory for sustainable development and focus has been shifted towards circular models, it appears that grape pomace consists a major value-adding component that can promote such economy schemes, as it can be reutilized in numerous ways across a number of industrial categories, including the winery that it came from. However, this study highlighted also the absence of a comprehensive legislative framework covering the addition of grape pomace in foods, of studies analyzing completely the cost of grape pomace revalorization, and of specific research on green/food-grade extraction methods of valuable compounds from grape pomace.
Graphic Abstract




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelhakam O, Elsebaie E, Ghazi A, Gouda M (2019) Quality characteristics of beef hamburger enriched with red grape pomace powder during freezing storage. Slov Vet Res 56(22 Suppl):333–373. https://doi.org/10.26873/SVR-772-2019
Acun S, Gül H (2014) Effects of grape pomace and grape seed flours on cookie quality. Qual Assur Saf Crop Foods 6(1):81–88. https://doi.org/10.3920/QAS2013.0264
Aghamirzaei M, Peighambardoust SH, Azadmard-Damirchi S, Majzoob M (2018) Effects of grape seed powder as a functional ingredient on flour physicochemical characteristics and dough rheological properties. J Agric Sci Technol 17(2):365–373
Aksoylu Z, Çağindi Ö, Köse E (2015) Effects of blueberry, grape seed powder and poppy seed incorporation on physicochemical and sensory properties of biscuit. J Food Qual 38(3):164–174. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfq.12133
Aliakbarian B, Casale M, Paini M, Casazza AA, Lanteri S, Perego P (2015) Production of a novel fermented milk fortified with natural antioxidants and its analysis by NIR spectroscopy. LWT Food Sci Technol 62(1):376–383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2014.07.037
American Association of Cereal Chemists (AACC) (2001) The definition of dietary fiber. Report of the dietary fiber definition committee to the board of directors of the AAC 46:112–126.
Andrés AI, Petrón MJ, Adámez JD, López M, Timón ML (2017) Food by-products as potential antioxidant and antimicrobial additives in chill stored raw lamb patties. Meat Sci 129:62–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meatsci.2017.02.013
Antonić B, Jančíková S, Dordević D, Tremlová B (2020) Grape pomace valorization: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Foods 9(11):1627. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9111627
Avantaggiato G, Greco D, Damascelli A, Solfrizzo M, Visconti A (2014) Assessment of multi-mycotoxin adsorption efficacy of grape pomace. J Agric Food Chem 62(2):497–507. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf404179h
Baca-Bocanegra B, Gonçalves S, Nogales-Bueno J, Mansinhos I, Heredia FJ, Hernández-Hierro JM, Romano A (2022) Influence of wine ph and ethanol content on the fining efficacy of proteins from winemaking by-products. Foods 11(12):1688. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11121688
Bambeni T, Tayengwa T, Chikwanha OC, Manley M, Gouws PA, Marais J, Fawole OA, Mapiye C (2021) Biopreservative efficacy of grape (Vitis vinifera) and clementine mandarin orange (Citrus reticulata) by-product extracts in raw ground beef patties. Meat Sci 181:108609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meatsci.2021.108609
Barbaccia P, Busetta G, Barbera M, Alfonzo A, Garofalo G, Francesca N, Moscarelli A, Moschetti G, Settani L, Gaglio R (2022) Effect of grape pomace from red cultivar “Nero d’Avola” on the microbiological, physicochemical, phenolic profile and sensory aspects of ovine Vastedda-like stretched cheese. J Appl Microbiol 133(1):130–144. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.15354
Barrows JN, Lipman AL, Bailey CJ (2003) Color additives: FDA’s regulatory process and historical perspectives. Food Safety Magazine. October/November 2003 issue
Bautista-Ortín AB, Cano-Lechuga M, Ruiz-García Y, Gómez-Plaza E (2014) Interactions between grape skin cell wall material and commercial enological tannins. Pract Implic Food Chem 152:558–565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.12.009
Bautista-Ortín AB, Ruiz-Garcia Y, Marin F, Molero N, Apolinar-Valiente R, Gomez-Plaza E (2015) Remarkable proanthocyanidin adsorption properties of Monastrell pomace cell wall material highlight its potential use as an alternative fining agent in red wine production. J Agric Food Chem 63(2):620–633. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf503659y
Bautista-Ortín AB, Martínez-Hernández A, Ruiz-García Y, Gil-Muñoz R, Gómez-Plaza E (2016) Anthocyanins influence tannin–cell wall interactions. Food Chem 206:239–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.03.045
Bender ABB, Speroni CS, Salvador PR, Loureiro BB, Lovatto NM, Goulart FR, Lovatto MT, Miranda MZ, Silva LP, Penna NG (2017) Grape pomace skins and the effects of its inclusion in the technological properties of muffins. J Culin Sci Technol 15(2):143–157. https://doi.org/10.1080/15428052.2016.1225535
Bender ABB, Speroni CS, Moro KIB, Morisso FDP, dos Santos DR, da Silva LP, Penna NG (2020) Effects of micronization on dietary fiber composition, physicochemical properties, phenolic compounds, and antioxidant capacity of grape pomace and its dietary fiber concentrate. LWT 117:108652. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2019.108652
Benvenuti J, Fisch A, dos Santos JHZ, Gutterres M (2019) Silica-based adsorbent material with grape bagasse encapsulated by the sol–gel method for the adsorption of Basic Blue 41 dye. J Environ Chem Eng 7(5):103342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.103342
Beres C, Costa GN, Cabezudo I, da Silva-James NK, Teles AS, Cruz AP, Mellinger-Silva C, Tonon RV, Cabral LMC, Freitas SP (2017) Towards integral utilization of grape pomace from winemaking process: a review. Waste Manag 68:581–594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2017.07.017
Beres C, Freitas SP, de Oliveira Godoy RL, de Oliveira DCR, Deliza R, Iacomini M, Mellinger-Silva C, Cabral LMC (2019) Antioxidant dietary fibre from grape pomace flour or extract: Does it make any difference on the nutritional and functional value? J Funct Foods 56:276–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2019.03.014
Bianchi F, Cervini M, Giuberti G, Rocchetti G, Lucini L, Simonato B (2022) Distilled grape pomace as a functional ingredient in vegan muffins: effect on physicochemical, nutritional, rheological and sensory aspects. Int J Food Sci Technol 57(8):4847–4858. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijfs.15720
Bimbo F, Bonanno A, Nocella G, Viscecchia R, Nardone G, De Devitiis B, Carlucci D (2017) Consumers’ acceptance and preferences for nutrition-modified and functional dairy products: a systematic review. Appetite 113:141–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2017.02.031
Bindon KA, Smith PA (2013) Comparison of the affinity and selectivity of insoluble fibres and commercial proteins for wine proanthocyanidins. Food Chem 136(2):917–928. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.08.016
Birch CS, Bonwick GA (2019) Ensuring the future of functional foods. Int J Food Sci Technol 54(5):1467–1485. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijfs.14060
Bordiga M, Travaglia F, Locatelli M (2019a) Valorisation of grape pomace: an approach that is increasingly reaching its maturity–a review. Int J Food Sci Technol 54(4):933–942. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijfs.14118
Bordiga M, Montella R, Travaglia F, Arlorio M, Coïsson JD (2019b) Characterization of polyphenolic and oligosaccharidic fractions extracted from grape seeds followed by the evaluation of prebiotic activity related to oligosaccharides. Int J Food Sci Technol 54(4):1283–1291. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijfs.14109
Brahim M, Gambier F, Brosse N (2014) Optimization of polyphenols extraction from grape residues in water medium. Ind Crops Prod 52:18–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2013.10.030
Buja LM (2022) The history, science, and art of wine and the case for health benefits: perspectives of an oenophilic cardiovascular pathologist. Cardiovasc Pathol 60:107446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carpath.2022.107446
Bustos G, Moldes AB, Cruz JM, Domínguez JM (2004) Formulation of low-cost fermentative media for lactic acid production with Lactobacillus rhamnosus using vinification lees as nutrients. J Agric Food Chem 52(4):801–808. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf030429k
Bustamante MA, Moral R, Paredes C, Pérez-Espinosa A, Moreno-Caselles J, Pérez-Murcia MD (2008) Agrochemical characterisation of the solid by-products and residues from the winery and distillery industry. Waste manag 28(2):372–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2007.01.013
Carpes ST, Pereira D, Moura CD, Reis ASD, Silva LDD, Oldoni TLC, Almeida JF, Plata-Oviedo MVS (2020) Lyophilized and microencapsulated extracts of grape pomace from winemaking industry to prevent lipid oxidation in chicken pâté. Braz J Food Technol 23:e2019112. https://doi.org/10.1590/1981-6723.11219
Carullo G, Spizzirri UG, Loizzo MR, Leporini M, Sicari V, Aiello F, Restuccia D (2020) Valorization of red grape (Vitis vinifera cv. Sangiovese) pomace as functional food ingredient. Ital J Food Sci. https://doi.org/10.14674/IJFS-1758
Carullo G, Spizzirri UG, Montopoli M, Cocetta V, Armentano B, Tinazzi M, Sciubba F, Giorgi G, Di Cocco ME, Bohn T, Aiello F, Restuccia D (2022) Milk kefir enriched with inulin-grafted seed extract from white wine pomace: chemical characterisation, antioxidant profile and in vitro gastrointestinal digestion. Int J Food Sci Technol 57(7):4086–4095. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijfs.15724
Carvalho FL, Pinto D, Schio RR, Dos Santos JP, Ketzer F, Silva LF, Dotto GL (2022) Polishing of painting process effluents through adsorption with biochar from winemaking residues. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(44):66348–66358. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20488-4
Cebrián-Tarancón C, Sánchez-Gómez R, Oliva J, Cámara MA, Zalacain A, Salinas MR (2021) Evolution of fungicide residues in pruned vine-shoots. OENO One 55(1):145–152. https://doi.org/10.20870/oeno-one.2021.55.1.4488
Chacar S, Itani T, Hajal J, Saliba Y, Louka N, Faivre JF, Maroun R, Fares N (2018) The impact of long-term intake of phenolic compounds-rich grape pomace on rat gut microbiota. J Food Sci 83(1):246–251. https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.14006
Choi YS, Choi JH, Han DJ, Kim HY, Lee MA, Jeong JY, Chung HJ, Kim CJ (2010a) Effects of replacing pork back fat with vegetable oils and rice bran fiber on the quality of reduced-fat frankfurters. Meat Sci 84(3):557–563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meatsci.2009.10.012
Choi YS, Choi JH, Han DJ, Kim HY, Lee MA, Kim HW, Lee JW, Chung HJ, Kim CJ (2010b) Optimization of replacing pork back fat with grape seed oil and rice bran fiber for reduced-fat meat emulsion systems. Meat Sci 84(1):212–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meatsci.2009.08.048
Chouchouli V, Kalogeropoulos N, Konteles SJ, Karvela E, Makris DP, Karathanos VT (2013) Fortification of yoghurts with grape (Vitis vinifera) seed extracts. LWT Food Sci Technol 53(2):522–529. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2013.03.008
Chowdhary P, Gupta A, Gnansounou E, Pandey A, Chaturvedi P (2021) Current trends and possibilities for exploitation of Grape pomace as a potential source for value addition. Environ Pollut 278:116796. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116796
Cilli LP, Contini LRF, Sinnecker P, Lopes PS, Andreo MA, Neiva CRP, Nascimento MS, Yoshida CMP, Venturini AC (2020) Effects of grape pomace flour on quality parameters of salmon burger. J Food Process Preserv 44(2):e14329. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpp.14329
Cohen SM, Eisenbrand G, Fukushima S, Gooderham NJ, Guengerich FP, Hecht SS et al (2020) GRAS 29 flavoring substances. Food Technol Mag 74(3):44–65
Corbin KR, Hsieh YSY, Betts NS, Byrt CS, Henderson M, Stork J, DeBolt S, Fincher GB, Burton RA (2015) Grape marc as a source of carbohydrates for bioethanol: chemical composition, pre-treatment and saccharification. Biores Technol 193:76–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.06.030
Costa JR, Amorim M, Vilas-Boas A, Tonon RV, Cabral LM, Pastrana L, Pintado M (2019) Impact of in vitro gastrointestinal digestion on the chemical composition, bioactive properties, and cytotoxicity of Vitis vinifera L. cv. Syrah grape pomace extract. Food Funct 10(4):1856–1869. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8FO02534G
Costa-Pérez A, Medina S, Sánchez-Bravo P, Domínguez-Perles R, García-Viguera C (2023) The (Poly) phenolic profile of separate winery by-products reveals potential antioxidant synergies. Molecules 28(5):2081. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052081
da Silva CM, da Boit Martinello K, Lütke SF, Godinho M, Perondi D, Silva LF, Dotto GL (2022a) Pyrolysis of grape bagasse to produce char for Cu (II) adsorption: a circular economy perspective. Biomass Convers Biorefin. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-022-02792-8
da Silva DJ, de Oliveira MM, Wang SH, Carastan DJ, Rosa DS (2022b) Designing antimicrobial polypropylene films with grape pomace extract for food packaging. Food Packag Shelf Life 34:100929. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fpsl.2022.100929
de Alencar MG, de Quadros CP, Luna ALLP, Neto AF, da Costa MM, Queiroz MAÁ, de Carvalho FAL, da Silva Araujo DH, Gois GC, dos Anjos Santos VL, da Silva Filho JRV, de Souza Rodrigues RT (2022) Grape skin flour obtained from wine processing as an antioxidant in beef burgers. Meat Sci 194:108963. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meatsci.2022.108963
de Azevedo PODS, Aliakbarian B, Casazza AA, LeBlanc JG, Perego P, de Souza Oliveira RP (2018) Production of fermented skim milk supplemented with different grape pomace extracts: effect on viability and acidification performance of probiotic cultures. PharmaNutrition 6(2):64–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phanu.2018.03.001
de Oliveira AP, Módenes AN, Bragião ME, Hinterholz CL, Trigueros DE, Isabella GDO (2018) Use of grape pomace as a biosorbent for the removal of the Brown KROM KGT dye. Bioresour Technol Rep 2:92–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biteb.2018.05.001
De Iseppi A, Marangon M, Vincenzi S, Lomolino G, Curioni A, Divol B (2021) A novel approach for the valorization of wine lees as a source of compounds able to modify wine properties. LWT 136:110274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2020.110274
Demirkol M, Tarakci Z (2018) Effect of grape (Vitis labrusca L.) pomace dried by different methods on physicochemical, microbiological and bioactive properties of yoghurt. LWT 97:770–777. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2018.07.058
Deng Q, Penner MH, Zhao Y (2011) Chemical composition of dietary fiber and polyphenols of five different varieties of wine grape pomace skins. Food Res Int 44(9):2712–2720. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2011.05.026
Elkatry HO, Ahmed AR, El-Beltagi HS, Mohamed HI, Eshak NS (2022) Biological activities of grape seed by-products and their potential use as natural sources of food additives in the production of Balady bread. Foods 11(13):1948. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11131948
Failla S, Restuccia A (2014) Methane potentials from grape marc by a laboratory scale plant. Appl Math Sci 8:6665–6678. https://doi.org/10.12988/ams.2014.474551
FDA (2023). GRAS Notices. https://www.cfsanappsexternal.fda.gov/scripts/fdcc/?set=GRASNotices
Fernandes JM, Calado T, Guimarães A, Rodrigues MAM, Abrunhosa L (2019) In vitro adsorption of aflatoxin B1, ochratoxin A, and zearalenone by micronized grape stems and olive pomace in buffer solutions. Mycotoxin Res 35:243–252. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12550-019-00349-9
Fernández CM, Ramos MJ, Pérez Á, Rodríguez JF (2010) Production of biodiesel from winery waste: extraction, refining and transesterification of grape seed oil. Biores Technol 101(18):7019–7024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.04.014
Ferreira SM, Santos L (2022) A potential valorization strategy of wine industry by-products and their application in cosmetics—case study: grape pomace and grapeseed. Molecules 27(3):969. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27030969
Ferri M, Vannini M, Ehrnell M, Eliasson L, Xanthakis E, Monari S, Sisti L, Marchese P, Celli A, Tassoni A (2020) From winery waste to bioactive compounds and new polymeric biocomposites: a contribution to the circular economy concept. J Adv Res 24:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jare.2020.02.015
Fontana M, Murowaniecki Otero D, Pereira AM, Santos RB, Gularte MA (2022) Grape pomace flour for incorporation into cookies: Evaluation of nutritional, sensory and technological characteristics. J Culin Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1080/15428052.2022.2086956
Fotakis C, Zervou M (2016) NMR metabolic fingerprinting and chemometrics driven authentication of Greek grape marc spirits. Food Chem 196:760–768. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.10.002
Frumento D, do Espirito Santo AP, Aliakbarian B, Casazza AA, Gallo M, Converti A, Perego P, (2013) Development of milk fermented with Lactobacillus acidophilus fortified with Vitis vinifera marc flour. Food Technol Biotechnol 51(3):370–375
Gaita C, Alexa E, Moigradean D, Conforti F, Poiana MA (2020) Designing of high value-added pasta formulas by incorporation of grape pomace skins. Rom Biotechnol Lett 25(3):1607–1614. https://doi.org/10.25083/rbl/25.3/1607.1614
Galanakis CM, Goulas V, Tsakona S, Manganaris GA, Gekas V (2013) A knowledge base for the recovery of natural phenols with different solvents. Int J Food Prop 16(2):382–396. https://doi.org/10.1080/10942912.2010.522750
Garcia-Lomillo J, González-SanJosé ML, Skibsted LH, Jongberg S (2016) Effect of skin wine pomace and sulfite on protein oxidation in beef patties during high oxygen atmosphere storage. Food Bioproc Technol 9(3):532–542. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-015-1649-y
Garcia-Lomillo J, Viegas O, Gonzalez-SanJose ML, Ferreira IM (2017a) Influence of red wine pomace seasoning and high-oxygen atmosphere storage on carcinogens formation in barbecued beef patties. Meat Sci 125:10–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meatsci.2016.11.009
Garcia-Lomillo J, Del Pino-García R, Muñiz-Rodríguez P (2017b) Alternative natural seasoning to improve the microbial stability of low-salt beef patties. Food Chem 227:122–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.01.070
Garcia-Martinez DJ, Calzada Funes J, Martin Saborido C, Santos C (2022) Grape polyphenols to arrest in vitro proliferation of human leukemia cells: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Food Rev Int 38(4):402–419. https://doi.org/10.1080/87559129.2020.1810700
Garrido J, Borges F (2013) Wine and grape polyphenols—a chemical perspective. Food Res Int 54(2):1844–1858. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2013.08.002
Garrido MD, Auqui M, Martí N, Linares MB (2011) Effect of two different red grape pomace extracts obtained under different extraction systems on meat quality of pork burgers. LWT Food Sci Technol 44(10):2238–2243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2011.07.003
Genisheva Z, Mussatto SI, Oliveira JM, Teixeira JA (2011) Evaluating the potential of wine-making residues and corn cobs as support materials for cell immobilization for ethanol production. Ind Crops Prod 34(1):979–985. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2011.03.006
Genisheva Z, Macedo S, Mussatto SI, Teixeira JA, Oliveira JM (2012) Production of white wine by Saccharomyces cerevisiae immobilized on grape pomace. J Inst Brew 118(2):163–173. https://doi.org/10.1002/jib.29
Genisheva Z, Mussatto SI, Oliveira JM, Teixeira JA (2013) Malolactic fermentation of wines with immobilised lactic acid bacteria–influence of concentration, type of support material and storage conditions. Food Chem 138(2–3):1510–1514. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.11.058
Genisheva Z, Teixeira JA, Oliveira JM (2014a) Immobilized cell systems for batch and continuous winemaking. Trends Food Sci Technol 40(1):33–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2014.07.009
Genisheva Z, Mota A, Mussatto SI, Oliveira JM, Teixeira JA (2014b) Integrated continuous winemaking process involving sequential alcoholic and malolactic fermentations with immobilized cells. Process Biochem 49(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2013.10.005
Genisheva Z, Vilanova M, Mussatto SI, Teixeira JA, Oliveira JM (2014c) Consecutive alcoholic fermentations of white grape musts with yeasts immobilized on grape skins–effect of biocatalyst storage and SO2 concentration on wine characteristics. LWT Food Sci Technol 59(2):1114–1122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2014.06.046
Gil M, Barrio-Galán D, Ubeda C, Peña-Neira Á (2018) Effectiveness of fibers from “Cabernet Sauvignon” (Vitis vinifera) pomace as fining agents for red wines. J Food Qual 2018:6408734. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/6408734
Gil-Muñoz R, Jiménez-Martínez MD, Bautista-Ortín AB, Gómez-Plaza E (2019) Effect of the use of purified grape pomace as a fining agent on the volatile composition of monastrell wines. Molecules 24(13):2423. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24132423
Glampedaki P, Dutschk V (2014) Stability studies of cosmetic emulsions prepared from natural products such as wine, grape seed oil and mastic resin. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 460:306–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2014.02.048
Gordillo B, Chamizo-González F, González-Miret ML, Heredia FJ (2021) Impact of alternative protein fining agents on the phenolic composition and color of Syrah red wines from warm climate. Food Chem 342:128297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128297
Górnaś P, Rudzińska M (2016) Seeds recovered from industry by-products of nine fruit species with a high potential utility as a source of unconventional oil for biodiesel and cosmetic and pharmaceutical sectors. Ind Crops Prod 83:329–338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.01.021
Gowman A, Wang T, Rodriguez-Uribe A, Mohanty AK, Misra M (2018) Bio-poly(butylene succinate) and its composites with grape pomace: mechanical performance and thermal properties. ACS Omega 3(11):15205–15216. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.8b01675
Gowman A, Rodriguez-Uribe A, Defersha F, Mohanty AK, Misra M (2020) Statistical design of sustainable composites from poly(lactic acid) and grape pomace. J Appl Polym Sci 137(36):49061. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.49061
Goyal S, Esposito M, Kapoor A (2018) Circular economy business models in developing economies: lessons from India on reduce, recycle, and reuse paradigms. Thunderbird Int Bus Rev 60(5):729–740. https://doi.org/10.1002/tie.21883
Guerrero RF, Smith P, Bindon KA (2013) Application of insoluble fibers in the fining of wine phenolics. J Agric Food Chem 61(18):4424–4432. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf400172f
Hoye C Jr, Ross CF (2011) Total phenolic content, consumer acceptance, and instrumental analysis of bread made with grape seed flour. J Food Sci 76(7):S428–S436. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1750-3841.2011.02324.x
Ilyas T, Chowdhary P, Chaurasia D, Gnansounou E, Pandey A, Chaturvedi P (2021) Sustainable green processing of grape pomace for the production of value-added products: an overview. Environ Technol Innov 23:101592. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2021.101592
Iyyappan J, Gurunathan B, Gopinath M, Vaishnavi A, Prathiba S, Kanishka V, Gomathi K, Dhithya V (2022) Advances and sustainable conversion of waste lignocellulosic biomass into biofuels. In: Gurunathan B, Sahadevan R (eds) Biofuels and bioenergy. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 167–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/C2020-0-02574-0
Jara-Palacios MJ (2019) Wine lees as a source of antioxidant compounds. Antioxidants 8(2):45. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8020045
Jiang Y, Simonsen J, Zhao Y (2011) Compression-molded biocomposite boards from red and white wine grape pomaces. J Appl Polym Sci 119:2834–2846. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.32961
Jiménez-Martínez MD, Gómez-Plaza E, Molero N, Bautista-Ortín AB (2017) Fining of red wines with pomace cell wall material: effect on wine phenolic composition. Food Bioprocess Technol 10(8):1531–1539. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-017-1922-3
Jiménez-Martínez MD, Gil-Muñoz R, Gómez-Plaza E, Bautista-Ortín AB (2018) Performance of purified grape pomace as a fining agent to reduce the levels of some contaminants from wine. Food Addit Contam Part A 35(6):1061–1070. https://doi.org/10.1080/19440049.2018.1459050
Jiménez-Martínez MD, Bautista-Ortín AB, Gil-Muñoz R, Gómez-Plaza E (2019a) Fining with purified grape pomace. Effect of dose, contact time and varietal origin on the final wine phenolic composition. Food Chem 271:570–576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.08.009
Jiménez-Martínez MD, Bautista-Ortín AB, Gil-Muñoz R, Gómez-Plaza E (2019b) Comparison of fining red wines with purified grape pomace versus commercial fining agents: effect on wine chromatic characteristics and phenolic content. Int J Food Sci Technol 54(4):1018–1026. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijfs.13881
Jin Q, O’Hair J, Stewart AC, O’Keefe SF, Neilson AP, Kim YT, McGuire M, Lee A, Wilder G, Huang H (2019) Compositional characterization of different industrial white and red grape pomaces in Virginia and the potential valorization of the major components. Foods 8(12):667. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8120667
Jin Q, Wang Z, Feng Y, Kim YT, Stewart AC, O’Keefe SF, Neilson AP, He Z, Huang H (2020) Grape pomace and its secondary waste management: biochar production for a broad range of lead (Pb) removal from water. Environ Res 186:109442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.109442
Kafantaris I, Stagos D, Kotsampasi B, Hatzis A, Kypriotakis A, Gerasopoulos K, Makri S, Goutzourelas N, Mitsagga C, Giavasis I, Petrotos K, Kokkas S, Goulas P, Christodoulou V, Kouretas D (2018) Grape pomace improves performance, antioxidant status, fecal microbiota and meat quality of piglets. Animal 12(2):246–255. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1751731117001604
Kandylis P (2022) Phytochemicals and antioxidant properties of edible flowers. Appl Sci 12(19):9937. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12199937
Kandylis P, Dimitrellou D, Moschakis T (2021) Recent applications of grapes and their derivatives in dairy products. Trends Food Sci Technol 114:696–711. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2021.05.029
Kaur S, Das M (2011) Functional foods: an overview. Food Sci Biotechnol 20(4):861–875. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-011-0121-7
Kokkinomagoulos E, Kandylis P (2020) Sustainable exploitation of by-products of vitivinicultural origin in winemaking. Proc 67(1):5. https://doi.org/10.3390/ASEC2020-07521
Kopsahelis N, Dimou C, Papadaki A, Xenopoulos E, Kyraleou M, Kallithraka S, Kotseridis Y, Papanikolaou S, Koutinas AA (2018) Refining of wine lees and cheese whey for the production of microbial oil, polyphenol-rich extracts and value-added co-products. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 93(1):257–268. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.5348
Korz S, Sadzik S, More C, Buchmann C, Richling E, Munoz K (2023) Effect of grape pomace varieties and soil characteristics on the leaching potential of total carbon, nitrogen and polyphenols. Soil Syst 7(2):49. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems7020049
Kourkoutas Y, Bekatorou A, Banat IM, Marchant R, Koutinas AA (2004) Immobilization technologies and support materials suitable in alcohol beverages production: a review. Food Microbiol 21(4):377–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fm.2003.10.005
Lavelli V, Harsha PS, Torri L, Zeppa G (2014) Use of winemaking by-products as an ingredient for tomato puree: the effect of particle size on product quality. Food Chem 152:162–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.11.103
León-González AJ, Jara-Palacios MJ, Abbas M, Heredia FJ, Schini-Kerth VB (2017) Role of epigenetic regulation on the induction of apoptosis in Jurkat leukemia cells by white grape pomace rich in phenolic compounds. Food Funct 8(11):4062–4069. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7fo00263g
Llobera A, Cañellas J (2008) Antioxidant activity and dietary fibre of Prensal Blanc white grape (Vitis vinifera) by‐products. Int J Food Sci Technol 43(11):1953–1959. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2621.2008.01798.x
Macagnan FT, da Silva LP, Hecktheuer LH (2016) Dietary fibre: the scientific search for an ideal definition and methodology of analysis, and its physiological importance as a carrier of bioactive compounds. Food Res Int 85:144–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2016.04.032
Machado N, Domínguez-Perles R (2017) Addressing facts and gaps in the phenolics chemistry of winery by-products. Molecules 22(2):286. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22020286
Mainente F, Menin A, Alberton A, Zoccatelli G, Rizzi C (2019) Evaluation of the sensory and physical properties of meat and fish derivatives containing grape pomace powders. Int J Food Sci Technol 54(4):952–958. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijfs.13850
Mallouchos A, Reppa P, Aggelis G, Kanellaki M, Koutinas AA, Komaitis M (2002) Grape skins as a natural support for yeast immobilization. Biotechnol Lett 24(16):1331–1335. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1019892232296
Manca ML, Casula E, Marongiu F, Bacchetta G, Sarais G, Zaru M, Escribano-Ferrer E, Peris JE, Usach I, Fais S, Scano A, Orrù G, Maroun RG, Fadda AM, Manconi M (2020) From waste to health: Sustainable exploitation of grape pomace seed extract to manufacture antioxidant, regenerative and prebiotic nanovesicles within circular economy. Sci Rep 10(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-71191-8
Maner S, Sharma AK, Banerjee K (2017) Wheat flour replacement by wine grape pomace powder positively affects physical, functional and sensory properties of cookies. Proc Natl Acad Sci India Sect B Biol Sci 87:109–113. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-015-0570-5
Marchiani R, Bertolino M, Belviso S, Giordano M, Ghirardello D, Torri L, Piochi M, Zeppa G (2016a) Yogurt enrichment with grape pomace: effect of grape cultivar on physicochemical, microbiological and sensory properties. J Food Qual 39(2):77–89. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfq.12181
Marchiani R, Bertolino M, Ghirardello D, McSweeney PL, Zeppa G (2016b) Physicochemical and nutritional qualities of grape pomace powder-fortified semi-hard cheeses. J Food Sci Technol 53(3):1585–1596. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-015-2105-8
Marín-Benito JM, Brown CD, Herrero-Hernández E, Arienzo M, Sánchez-Martín MJ, Rodríguez-Cruz MS (2013) Use of raw or incubated organic wastes as amendments in reducing pesticide leaching through soil columns. Sci Total Environ 463:589–599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.06.051
Marinelli V, Padalino L, Nardiello D, Del Nobile MA, Conte A (2015) New approach to enrich pasta with polyphenols from grape marc. J Chem 2015:734578. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/734578
Martínez Salgado MM, Blu RO, Janssens M, Fincheira P (2019) Grape pomace compost as a source of organic matter: evolution of quality parameters to evaluate maturity and stability. J Clean Prod 216:56–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.01.156
Meini MR, Cabezudo I, Galetto CS, Romanini D (2021) Production of grape pomace extracts with enhanced antioxidant and prebiotic activities through solid-state fermentation by Aspergillus niger and Aspergillus oryzae. Food Biosci 42:101168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbio.2021.101168
Meral R, Doğan İS (2013) Grape seed as a functional food ingredient in bread-making. Int J Food Sci Nutr 64(3):372–379. https://doi.org/10.3109/09637486.2012.738650
Mielnik MB, Olsen E, Vogt G, Adeline D, Skrede G (2006) Grape seed extract as antioxidant in cooked, cold stored turkey meat. LWT Food Sci Technol 39(3):191–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2005.02.003
Milinčić DD, Stanisavljević NS, Kostić AŽ, Gašić UM, Stanojević SP, Tešić ŽL, Pešić MB (2022) Bioaccessibility of phenolic compounds and antioxidant properties of goat-milk powder fortified with grape-pomace-seed extract after in vitro gastrointestinal digestion. Antioxidants 11(11):2164. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11112164
Mohamed Ahmed IA, Özcan MM, Al Juhaimi F, Babiker EFE, Ghafoor K, Banjanin T, Osman MA, Gassem MA, Alqaf HAS (2020) Chemical composition bioactive compounds mineral contents and fatty acid composition of pomace powder of different grape varieties. J Food Process Preserv 44(7):e14539. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpp.14539
Moreno-García J, García-Martínez T, Mauricio JC, Moreno J (2018) Yeast immobilization systems for alcoholic wine fermentations: actual trends and future perspectives. Front Microbiol 9:241. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.00241
Nakov G, Brandolini A, Hidalgo A, Ivanova N, Stamatovska V, Dimov I (2020) Effect of grape pomace powder addition on chemical, nutritional and technological properties of cakes. LWT 134:109950. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2020.109950
Nash V, Ranadheera CS, Georgousopoulou EN, Mellor DD, Panagiotakos DB, McKune AJ, Kellett J, Naumovski N (2018) The effects of grape and red wine polyphenols on gut microbiota–a systematic review. Food Res Int 113:277–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2018.07.019
Nayak A, Bhushan B, Rodriguez-Turienzo L (2018) Recovery of polyphenols onto porous carbons developed from exhausted grape pomace: a sustainable approach for the treatment of wine wastewaters. Water Res 145:741–756. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.09.017
Nendel C, Reuter S (2007) Kinetics of net nitrogen mineralisation from soil-applied grape residues. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 79:233–241. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-007-9110-x
Nikolaou A, Kourkoutas Y (2021) High-temperature semi-dry and sweet low alcohol wine-making using immobilized kefir culture. Fermentation 7(2):45. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation7020045
Nikolaou A, Tsakiris A, Kanellaki M, Bezirtzoglou E, Akrida-Demertzi K, Kourkoutas Y (2019) Wine production using free and immobilized kefir culture on natural supports. Food Chem 272:39–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.08.015
Nikolaou A, Sgouros G, Mitropoulou G, Santarmaki V, Kourkoutas Y (2020) Freeze-dried immobilized kefir culture in low alcohol winemaking. Foods 9(2):115. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9020115
Nikolaou A, Sgouros G, Santarmaki V, Mitropoulou G, Kourkoutas Y (2022) Preliminary evaluation of the use of thermally-dried immobilized kefir cells in low alcohol winemaking. Appl Sci 12(12):6176. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12126176
Nogueira GF, Soares IHBT, Soares CT, Fakhouri FM, de Oliveira RA (2022) Development and characterization of arrowroot starch films incorporated with grape pomace extract. Polysaccharides 3(1):250–263. https://doi.org/10.3390/polysaccharides3010014
Oak MH, Auger C, Belcastro E, Park SH, Lee HH, Schini-Kerth VB (2018) Potential mechanisms underlying cardiovascular protection by polyphenols: role of the endothelium. Free Radic Biol Med 122:161–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.03.018
Ohashi T, Sugimoto K, Sasaki Y, Hisamoto M (2023) Effect of wine pomace extract on dechlorination of chloroethenes in soil suspension. Bioresour Bioprocess 10(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40643-023-00643-6
OIV (2020) Wine Production First Estimates. https://www.greatwinecapitals.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/OIV-2020-World-Wine-Production-First-Estimates-presentation-pdf.pdf. Accessed 1 Aug 2022
Oliveira M, Duarte E (2016) Integrated approach to winery waste: waste generation and data consolidation. Front Environ Sci Eng 10(1):168–176. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-014-0693-6
Oliveira DM, Marques DR, Kwiatkowski A, Monteiro ARG, Clemente E (2013) Sensory analysis and chemical characterization of cereal enriched with grape peel and seed flour. Acta Sci Technol 35(3):427–431. https://doi.org/10.4025/actascitechnol.v35i3.13176
Oprea OB, Popa ME, Apostol L, Gaceu L (2022) Research on the potential use of grape seed flour in the bakery industry. Foods 11(11):1589. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11111589
Ortega-Heras M, Gómez I, de Pablos-Alcalde S, González-Sanjosé ML (2019) Application of the just-about-right scales in the development of new healthy whole-wheat muffins by the addition of a product obtained from white and red grape pomace. Foods 8(9):419. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8090419
Osete-Alcaraz A, Osete-Alcaraz L, Ortega-Regules AE, Bautista-Ortín AB, Gómez-Plaza E (2022) Grape pulp fiber as possible fining agents for red wine. Biomolecules 12(10):1519. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12101519
Özvural EB, Vural H (2014) Which is the best grape seed additive for frankfurters: Extract, oil or flour? J Sci Food Agric 94(4):792–797. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.6442
Pellera FM, Acheilas I, Gidarakos E (2015) Low-temperature thermal treatment of lignocellulosic waste prior to anaerobic digestion. In: Proceedings of the 14th international conference on environmental science and technology. Rhodes, Greece
Peñas E, Di Lorenzo C, Uberti F, Restani P (2015) Allergenic proteins in enology: a review on technological applications and safety aspects. Molecules 20(7):13144–13164. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules200713144
Pereira A, Lee HC, Lammert R Jr, Wolberg C Jr, Ma D, Immoos C, Casassa F, Kang I (2022) Effects of red-wine grape pomace on the quality and sensory attributes of beef hamburger patty. Int J Food Sci Technol 57(3):1814–1823. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijfs.15559
Pérez-Bibbins B, Torrado-Agrasar A, Pérez-Rodríguez N, Aguilar-Uscanga MG, Domínguez JM (2015a) Evaluation of the liquid, solid and total fractions of beer, cider and wine lees as economic nutrient for xylitol production. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 90(6):1027–1039. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.4405
Pérez-Bibbins B, Torrado-Agrasar A, Salgado JM, de Souza Oliveira RP, Domínguez JM (2015b) Potential of lees from wine, beer and cider manufacturing as a source of economic nutrients: an overview. Waste Manag 40:72–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2015.03.009
Pini F, Aquilani C, Giovannetti L, Viti C, Pugliese C (2020) Characterization of the microbial community composition in Italian Cinta Senese sausages dry-fermented with natural extracts as alternatives to sodium nitrite. Food Microbiol 89:103417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fm.2020.103417
Priyadarshi R, Kim SM, Rhim JW (2021) Carboxymethyl cellulose-based multifunctional film combined with zinc oxide nanoparticles and grape seed extract for the preservation of high-fat meat products. Sustain Mater Technol 29:e00325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.susmat.2021.e00325
Quideau S, Deffieux D, Douat-Casassus C, Pouységu L (2011) Plant polyphenols: chemical properties, biological activities, and synthesis. Angew Chem Int Ed 50(3):586–621. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201000044
Rainero G, Bianchi F, Rizzi C, Cervini M, Giuberti G, Simonato B (2022) Breadstick fortification with red grape pomace: effect on nutritional, technological and sensory properties. J Sci Food Agric 102(6):2545–2552. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.11596
Rasines-Perea Z, Teissedre PL (2017) Grape polyphenols’ effects in human cardiovascular diseases and diabetes. Molecules 22(1):68. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22010068
Renaud SD, de Lorgeril M (1992) Wine, alcohol, platelets, and the French paradox for coronary heart disease. Lancet 339(8808):1523–1526. https://doi.org/10.1016/0140-6736(92)91277-f
Riazi F, Zeynali F, Hoseini E, Behmadi H, Savadkoohi S (2016) Oxidation phenomena and color properties of grape pomace on nitrite-reduced meat emulsion systems. Meat Sci 121:350–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meatsci.2016.07.008
Ribéreau-Gayon P, Glories Y, Maujean A, Dubourdieu D (2021) Handbook of enology, volume 2: the chemistry of wine stabilization and treatments, 3rd edn. John Wiley & Sons, New York
Rivas B, Torrado A, Moldes AB, Domínguez JM (2006) Tartaric acid recovery from distilled lees and use of the residual solid as an economic nutrient for Lactobacillus. J Agric Food Chem 54(20):7904–7911. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf061617o
Rogiers SY, Greer DH, Liu Y, Baby T, Xiao Z (2022) Impact of climate change on grape berry ripening: an assessment of adaptation strategies for the Australian vineyard. Front Plant Sci 13:1094633. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2022.1094633
Rosales Soto MU, Brown K, Ross CF (2012) Antioxidant activity and consumer acceptance of grape seed flour-containing food products. Int J Food Sci Technol 47(3):592–602. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2621.2011.02882.x
Rózek A, Achaerandio I, Güell C, López F, Ferrando M (2010) Use of commercial grape phenolic extracts to supplement solid foodstuff. LWT Food Sci Technol 43(4):623–631. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2009.11.002
Ryu KS, Shim KS, Shin D (2014) Effect of grape pomace powder addition on TBARS and color of cooked pork sausages during storage. Korean J Food Sci Anim Resour 34(2):200. https://doi.org/10.5851/kosfa.2014.34.2.200
Saberi M, Saremnezhad S, Soltani M, Faraji A (2023) Functional stirred yogurt manufactured using co-microencapsulated or free forms of grape pomace and flaxseed oil as bioactive ingredients: physicochemical, antioxidant, rheological, microstructural, and sensory properties. Food Sci Nutr. https://doi.org/10.1002/fsn3.3385
Sagdic O, Ozturk I, Cankurt H, Tornuk F (2012) Interaction between some phenolic compounds and probiotic bacterium in functional ice cream production. Food Bioproc Technol 5(8):2964–2971. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-011-0611-x
Samohvalova O, Grevtseva N, Brykova T, Grigorenko A (2016) The effect of grape seed powder on the quality of butter biscuits. East Eur J Enterp Technol 3(11):61–66. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2016.69838
Sánchez-Alonso I, Borderías AJ (2008a) Technological effect of red grape antioxidant dietary fibre added to minced fish muscle. Int J Food Sci Technol 43(6):1009–1018. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2621.2007.01554.x
Sánchez-Alonso I, Borderías J, Larsson K, Undeland I (2007a) Inhibition of hemoglobin-mediated oxidation of regular and lipid-fortified washed cod mince by a white grape dietary fiber. J Agric Food Chem 55(13):5299–5305. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf0702242
Sánchez-Alonso I, Jiménez-Escrig A, Saura-Calixto F, Borderías AJ (2007b) Effect of grape antioxidant dietary fibre on the prevention of lipid oxidation in minced fish: evaluation by different methodologies. Food Chem 101(1):372–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2005.12.058
Sánchez-Alonso I, Solas MT, Borderías AJ (2007c) Physical study of minced fish muscle with a white-grape by-product added as an ingredient. J Food Sci 72(2):E94–E101. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1750-3841.2007.00273.x
Sánchez-Alonso I, Jiménez-Escrig A, Saura-Calixto F, Borderías AJ (2008b) Antioxidant protection of white grape pomace on restructured fish products during frozen storage. LWT Food Sci Technol 41(1):42–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2007.02.002
Sánchez-Gómez R, Sánchez-Vioque R, Santana-Méridas O, Martín-Bejerano M, Alonso GL, Salinas MR, Zalacain A (2017) A potential use of vine-shoot wastes: The antioxidant, antifeedant and phytotoxic activities of their aqueous extracts. Ind Crops Prod 97:120–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.12.009
Sancho-Galán P, Amores-Arrocha A, Jiménez-Cantizano A, Palacios V (2020) Physicochemical and nutritional characterization of winemaking lees: a new food ingredient. Agronomy 10(7):996. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10070996
Sant’Anna V, Christiano FDP, Marczak LDF, Tessaro IC, Thys RCS (2014) The effect of the incorporation of grape marc powder in fettuccini pasta properties. LWT Food Sci Technol 58(2):497–501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2014.04.008
Saurabh CK, Gupta S, Variyar PS (2018) Development of guar gum based active packaging films using grape pomace. J Food Sci Technol 55(6):1982–1992. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-018-3112-3
Sáyago-Ayerdi SG, Brenes A, Goñi I (2009) Effect of grape antioxidant dietary fiber on the lipid oxidation of raw and cooked chicken hamburgers. LWT Food Sci Technol 42(5):971–976. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2008.12.006
Schiavone S, Marchionni B, Bucci R, Marini F, Biancolillo A (2020) Authentication of Grappa (Italian grape marc spirit) by Mid and Near Infrared spectroscopies coupled with chemometrics. Vib Spectrosc 107:103040. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vibspec.2020.103040
Shlisky J, Bloom DE, Beaudreault AR, Tucker KL, Keller HH, Freund-Levi Y, Fiedling RA, Cheng FW, Jensen GL, Wu D, Meydani SN (2017) Nutritional considerations for healthy aging and reduction in age-related chronic disease. Adv Nutr 8(1):17. https://doi.org/10.3945/an.116.013474
Šikuten I, Štambuk P, Andabaka Ž, Tomaz I, Marković Z, Stupić D, Maletić E, Kontić JK, Preiner D (2020) Grapevine as a rich source of polyphenolic compounds. Molecules 25(23):5604. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25235604
Smith IN, Yu J (2015) Nutritional and sensory quality of bread containing different quantities of grape pomace from different grape cultivars. EC Nutr 2(1):291–301
Solfrizzo M, Avantaggiato G, Panzarini G, Visconti A (2010) Removal of ochratoxin A from contaminated red wines by repassage over grape pomaces. J Agric Food Chem 58(1):317–323. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf9030585
Solomakou N, Goula AM (2021) Treatment of olive mill wastewater by adsorption of phenolic compounds. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 20(3):839–863. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-021-09585-x
Sousa EC, Uchôa-Thomaz AMA, Carioca JOB, Morais SMD, Lima AD, Martins CG, Alexandrino CD, Ferreira PAT, Rodrigues ALM, Rodrigues SP, Silva JDN, Rodrigues LL (2014) Chemical composition and bioactive compounds of grape pomace (Vitis vinifera L.), Benitaka variety, grown in the semiarid region of Northeast Brazil. Food Sci Technol 34(1):135–142. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0101-20612014000100020
Šporin M, Avbelj M, Kovač B, Možina SS (2018) Quality characteristics of wheat flour dough and bread containing grape pomace flour. Food Sci Technol Int 24(3):251–263. https://doi.org/10.1177/1082013217745398
Teixeira A, Baenas N, Dominguez-Perles R, Barros A, Rosa E, Moreno DA, Garcia-Viguera C (2014) Natural bioactive compounds from winery by-products as health promoters: a review. Int J Mol Sci 15(9):15638–15678. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms150915638
Theagarajan R, Malur Narayanaswamy L, Dutta S, Moses JA, Chinnaswamy A (2019) Valorisation of grape pomace (cv. Muscat) for development of functional cookies. Int J Food Sci Technol 54(4):1299–1305. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijfs.14119
Tolve R, Simonato B, Rainero G, Bianchi F, Rizzi C, Cervini M, Giuberti G (2021) Wheat bread fortification by grape pomace powder: nutritional, technological, antioxidant, and sensory properties. Foods 10(1):75. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10010075
Tremlova B, Havlova L, Benes P, Zemancova J, Buchtova H, Tesikova K, Dordevic S, Dordevic D (2022) Vegetarian “sausages” with the addition of grape flour. Appl Sci 12(4):2189. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12042189
Tsaousi K, Koutinas AA, Bekatorou A, Loukatos P (2010) Fermentation efficiency of cells immobilized on delignified brewers’ spent grains after low-and high-temperature thin layer thermal drying. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 162(2):594–606. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-009-8848-9
Tseng A, Zhao Y (2013) Wine grape pomace as antioxidant dietary fibre for enhancing nutritional value and improving storability of yogurt and salad dressing. Food Chem 138(1):356–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.09.148
Visconti A, Perrone G, Cozzi G, Solfrizzo M (2008) Managing ochratoxin A risk in the grape-wine food chain. Food Addit Contam 25(2):193–202. https://doi.org/10.1080/02652030701744546
Viveros A, Chamorro S, Pizarro M, Arija I, Centeno C, Brenes A (2011) Effects of dietary polyphenol-rich grape products on intestinal microflora and gut morphology in broiler chicks. Poult Sci 90(3):566–578. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps.2010-00889
Wine & Spirit Education Trust (2012) Wines and spirits: understanding style and quality, 2nd edn. Wine, London, p 278
Wittenauer J, Mäckle S, Sußmann D, Schweiggert-Weisz U, Carle R (2015) Inhibitory effects of polyphenols from grape pomace extract on collagenase and elastase activity. Fitoterapia 101:179–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2015.01.005
Xiong Y, Chen M, Warner RD, Fang Z (2020) Incorporating nisin and grape seed extract in chitosan-gelatine edible coating and its effect on cold storage of fresh pork. Food Control 110:107018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2019.107018
Xu Y, Willis S, Jordan K, Sismour E (2018) Chitosan nanocomposite films incorporating cellulose nanocrystals and grape pomace extracts. Packag Technol Sci 31(9):631–638. https://doi.org/10.1002/pts.2389
Yalcin E, Ozdal T, Gok I (2022) Investigation of textural, functional, and sensory properties of muffins prepared by adding grape seeds to various flours. J Food Process Preserv 46(5):e15316. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpp.15316
Yoon JY, Kim JE, Song HJ, Oh KB, Jo JW, Yang YH, Lee SH, Kang G, Kim HJ, Choi YK (2021) Assessment of adsorptive behaviors and properties of grape pomace-derived biochar as adsorbent for removal of cymoxanil pesticide. Environ Technol Innov 21:101242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2020.101242
Zacharof MP (2017) Grape winery waste as feedstock for bioconversions: applying the biorefinery concept. Waste Biomass Valoriz 8(4):1011–1025. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-016-9674-2
Zeng J, Zeng H, Wang Z (2022) Review on technology of making biofuel from food waste. Int J Energy Res 46(8):10301–10319. https://doi.org/10.1002/er.7868
Zhang Y, Huang K (2019) Grape pomace as a biosorbent for fluoride removal from groundwater. RSC Adv 9(14):7767–7776. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9RA00109C
Zhao D, Simon JE, Wu Q (2020) A critical review on grape polyphenols for neuroprotection: strategies to enhance bioefficacy. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 60(4):597–625. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2018.1546668
Zheng Y, Lee C, Yu C, Cheng YS, Simmons CW, Zhang R, Jenkins BM, VanderGheynst JS (2012) Ensilage and bioconversion of grape pomace into fuel ethanol. J Agric Food Chem 60(44):11128–11134. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf303509v
Zhu F, Du B, Zheng L, Li J (2015) Advance on the bioactivity and potential applications of dietary fibre from grape pomace. Food Chem 186:207–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.07.057
Zion Market Research (2023) Global wine market size to grow USD 583.77 billion by 2032. https://www.globenewswire.com/en/news-release/2023/06/01/2680178/0/en/Global-Wine-Market-Size-To-Grow-USD-583-77-Billion-by-2032-CAGR-of-5-7.html. Accessed 07 Jul 2023
Funding
The research work was supported by the Hellenic Foundation for Research and Innovation (HFRI) under the 3rd Call for HFRI PhD Fellowships (Fellowship Number: 6158).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
EK: manuscript writing—original draft, writing—review and editing, funding acquisition. PK: conceptualization, supervision, writing—review and editing, project administration, funding acquisition. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no potential conflict of interest with respect to the research, authorship or publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kokkinomagoulos, E., Kandylis, P. Grape pomace, an undervalued by-product: industrial reutilization within a circular economy vision. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 22, 739–773 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-023-09665-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-023-09665-0